Health Studies Hub
Your go-to source for daily breakdowns of the latest health, fitness, and nutrition research.
Screen Time Harms Kids’ Brains with Reward Overload.
In 2025, a review in PMC analyzed data from multiple studies, including the 2022 ABCD Study with 2,217 kids aged 9-10, using brain scans and behavior tests. It found excessive screen time, especially with reward-heavy games on devices like iPads, triggers dopamine overload, making kids crave instant gratification and struggle with everyday tasks. Kids with over 2 hours daily showed higher attention problems and depression scores, with brain scans revealing lower caudate nucleus activity (a reward area), hinting at addiction risks, and reduced prefrontal cortex function, linked to poor impulse control and increased aggression.
Probiotics Cut Weight and Fat in Obese Adults.
In 2024, Belén Torres and a team from Spain reviewed six clinical trials from 2012–2022 involving overweight or obese adults. They studied how probiotics, like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus strains, affect body weight, BMI, and fat mass without dieting, using data from PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane databases.
Daily Walking Cuts Chronic Back Pain Risk.
In 2025, Paul Jarle Mork and a team from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology studied 11,194 adults over time. They tracked walking habits and lower back problems, comparing those who walked more to those who walked less, focusing on daily minutes rather than speed.
Meat Lowers Cancer Risk and Outmuscles Soy by 2x.
In a 2025 study from McMaster University, researchers analyzed nearly 16,000 adults from NHANES III to check if animal protein raises death risk from heart disease, cancer, or any cause. They found no link to higher mortality—animal protein even cut cancer death risk by a modest but significant amount. Plant protein showed no strong effects, but inflammatory diets with processed meats worsened outcomes.
Unrecognized Ingredients Signal Body Trouble.
“If you don’t recognize an ingredient, neither does your body.”
~Jen Smiley
In a 2025 podcast interview on the Ultimate Human Podcast, hosted by Gary Brecka, nutrition expert Jen Smiley shared her journey to better health by reading food labels. She explained how grocery items are 98% marketing, with tiny ingredient lists hiding chemicals you can't pronounce, like preservatives that cause inflammation and disrupt your body's natural processes.
Handgrip Strength Signals Malnutrition Risk.
In 2025, Vânia Aparecida Leandro-Merhi and a team from Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas studied 211 hospitalized adults in Brazil’s public health system. They used the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) criteria and handgrip strength (HGS) to spot nutritional risks, comparing them to standard tools like Nutritional Risk Screening-2002, measuring muscle strength and body composition.
Artificial Sweeteners Linked to Higher Prostate Cancer Risk.
In 2025, Kuiyuan Zhang and a team from Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine analyzed data from public databases to study how artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin relate to prostate cancer. They used computer models and lab tests to find key genes and see how sweeteners interact with cancer cells.
High-Intensity Exercise Cuts Depression by 20-30%.
In 2025, J. Zeng and a team from China reviewed 9 randomized trials with 514 adults battling depression. They compared high-intensity exercise (like intense running or weight lifting) to control groups, measuring depression with standard scales like the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD). Workouts lasted from weeks to months.
Vitamin D And Exercise : The Ultimate Team to Protect Aging Brains.
In 2025, Jingfeng Chen and a team from Chinese universities reviewed animal and human studies on how vitamin D and exercise together help keep brains healthy as people age. They looked at things like brain growth proteins, blood flow, and swelling in the brain, focusing on older adults with memory problems.
Loneliness Worsens Diet Quality in Older Adults.
In 2025, Elena Freire Paz and a team from the University of Santiago de Compostela studied 25 older adults in Spain (Galicia and Extremadura) using interviews and home observations from November 2024 to April 2025. They explored how loneliness affects eating habits, focusing on food choices, cooking routines, and meal enjoyment.
Poor Sleep Drives Unhealthy Eating Choices.
In 2025, Andrea Bazzani and Ugo Faraguna from Italian universities wrote an editorial reviewing how eating and sleeping are linked. They looked at past studies showing poor sleep changes what we crave, like more sweets and high-calorie foods, due to hormone shifts like less leptin (fullness signal) and more ghrelin (hunger signal). This can lead to overeating and weight gain.
Exercise Cuts Chronic Pain and Boosts Mobility By Up To 30%.
In 2024, Harvard Health Publishing reviewed studies on how exercise helps chronic pain, like back pain or arthritis. They looked at how activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga affect pain levels, inflammation, and mood in adults with ongoing pain, drawing on clinical trials and expert insights.
Ziplock Bags Release Harmful Microplastics.
In 2024, Cheng Fang and a team from the University of Newcastle, Australia, studied micro- and nanoplastics (MNPs) released from self-sealing Ziploc bags used for food storage. Using scanning electron microscopy and Raman imaging, they found that opening and closing bags creates friction, releasing thousands of MNPs per use, ranging from hundreds of nanometers to millimeters.
Amino Acids May Feed Cancer Cells, Not Patients.
In 2025, Giovanni Corsetti and a team from the University of Brescia reviewed studies on amino acid (AA) supplements in cancer patients. They looked at how diet and obesity cause up to 50% of tumors, and how 30-90% of patients get malnutrition from the tumor's high energy use, leading to muscle loss and weakness called sarcopenia or cachexia.
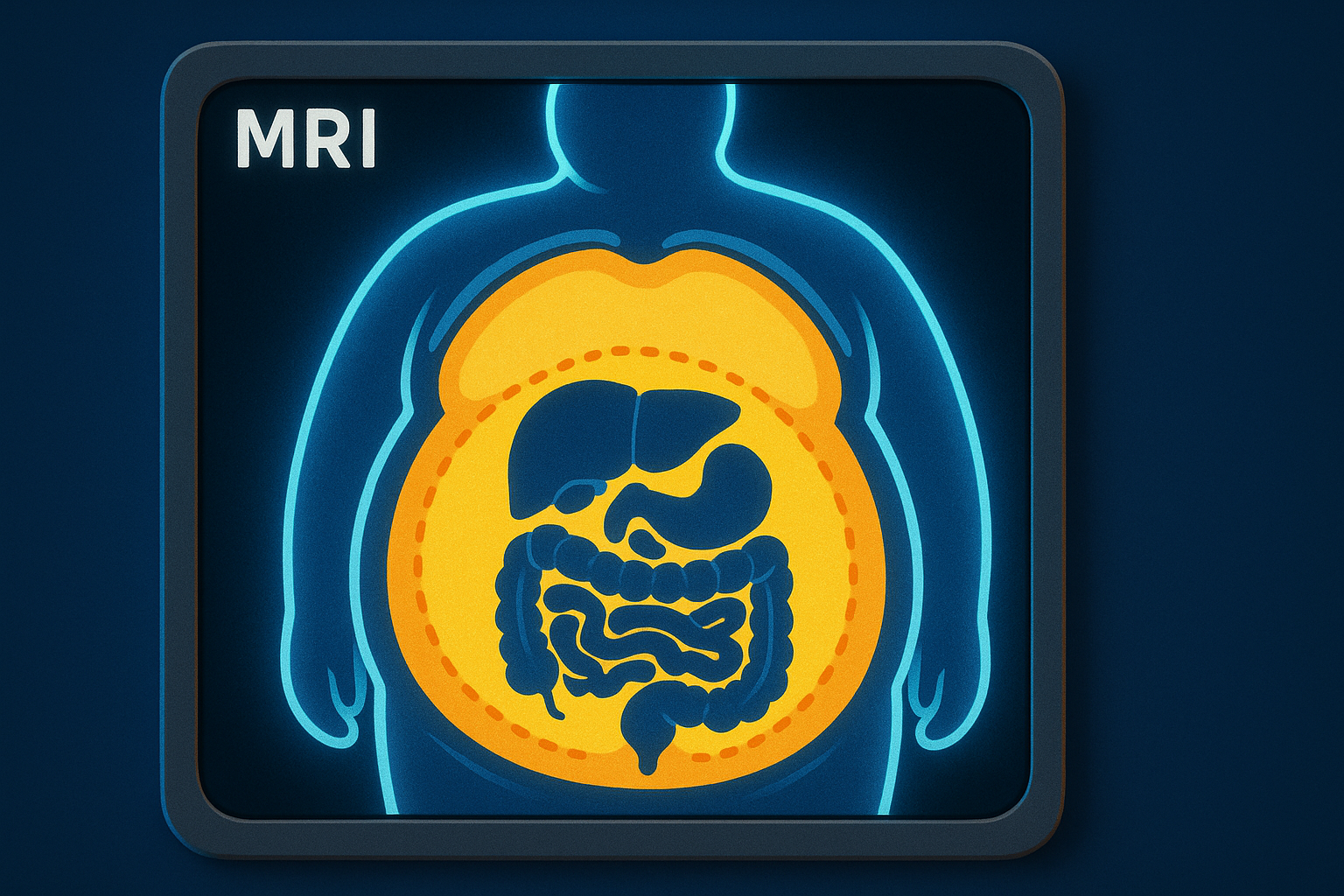
Hidden Visceral Fat Speeds Heart Aging Despite Exercise.
In 2025, Vladimir Losev and a team from the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences in London analyzed 21,241 UK Biobank adults, using AI to study body fat via whole-body imaging and heart health through scans. They focused on visceral fat (hidden around organs like the stomach) and its link to heart aging, measured by tissue stiffness and inflammation.
Metabolic Syndrome Hikes Parkinson’s Risk by 39%.
In 2025, X. Zhang and a team analyzed 467,200 adults aged 37–73 from the UK Biobank, tracking them for Parkinson’s disease (PD). They defined metabolic syndrome (MetS) as having at least three of: big waist (≥40 inches men, ≥34.6 inches women), high blood pressure, low HDL cholesterol, high triglycerides, or high blood sugar. They checked medical records for 3,222 PD cases.
Artificial Sweeteners Speed Up Brain Aging by 1.6 Years
In 2025, Claudia Kimie Suemoto and a team from the University of São Paulo in Brazil studied 12,772 middle-aged adults (average age 52) over several years. They tracked intake of seven sweeteners like aspartame and saccharin in ultra-processed foods such as diet sodas and yogurts, using food surveys and cognitive tests for memory and thinking skills.
High-Protein Breakfasts Ease Morning Anxiety.
In 2020, a scoping review by K. Ahern and team found that low protein intake and unstable blood sugar from high-carb diets worsened anxiety by 20-30%, as they disrupt serotonin production and spike stress hormones like cortisol. A 2016 study by K. M. Whitaker showed skipping breakfast raised cortisol levels in women by 15-25%, increasing morning stress and anxiety.
Gel Nail Polish Chemical TPO Poses Serious Health Risks.
In 2025, health experts reviewed animal and lab studies on trimethylbenzoyl diphenylphosphine oxide (TPO), a chemical in gel nail polishes banned in the EU but still used in the US. They examined TPO’s effects on reproduction, cancer risk, and skin reactions, using data from rat, rabbit, and human cell tests.
Exercise Slows Aging Clock in Multiple Organs.
In 2025, Takuji Kawamura and a team from Tohoku University reviewed studies on how exercise affects epigenetic aging, which shows how fast your body ages at the DNA level. They looked at human and animal research, focusing on structured workouts like running or weightlifting, using epigenetic clocks to measure DNA changes in blood, muscles, and other organs.