Health Studies Hub
Your go-to source for daily breakdowns of the latest health, fitness, and nutrition research.
Isometric Training Builds Muscle Effectively.
In 2019, Dustin J. Oranchuk and a team from Auckland University of Technology reviewed 26 studies with 713 participants on isometric training's long-term effects. They looked at how muscle length, intensity, and intent affect adaptations like muscle size, strength, and architecture over 3-14 weeks.
Daily Walking Cuts Chronic Back Pain Risk.
In 2025, Paul Jarle Mork and a team from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology studied 11,194 adults over time. They tracked walking habits and lower back problems, comparing those who walked more to those who walked less, focusing on daily minutes rather than speed.
Handgrip Strength Signals Malnutrition Risk.
In 2025, Vânia Aparecida Leandro-Merhi and a team from Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas studied 211 hospitalized adults in Brazil’s public health system. They used the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) criteria and handgrip strength (HGS) to spot nutritional risks, comparing them to standard tools like Nutritional Risk Screening-2002, measuring muscle strength and body composition.
High-Intensity Exercise Cuts Depression by 20-30%.
In 2025, J. Zeng and a team from China reviewed 9 randomized trials with 514 adults battling depression. They compared high-intensity exercise (like intense running or weight lifting) to control groups, measuring depression with standard scales like the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD). Workouts lasted from weeks to months.
Vitamin D And Exercise : The Ultimate Team to Protect Aging Brains.
In 2025, Jingfeng Chen and a team from Chinese universities reviewed animal and human studies on how vitamin D and exercise together help keep brains healthy as people age. They looked at things like brain growth proteins, blood flow, and swelling in the brain, focusing on older adults with memory problems.
Exercise Cuts Chronic Pain and Boosts Mobility By Up To 30%.
In 2024, Harvard Health Publishing reviewed studies on how exercise helps chronic pain, like back pain or arthritis. They looked at how activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga affect pain levels, inflammation, and mood in adults with ongoing pain, drawing on clinical trials and expert insights.
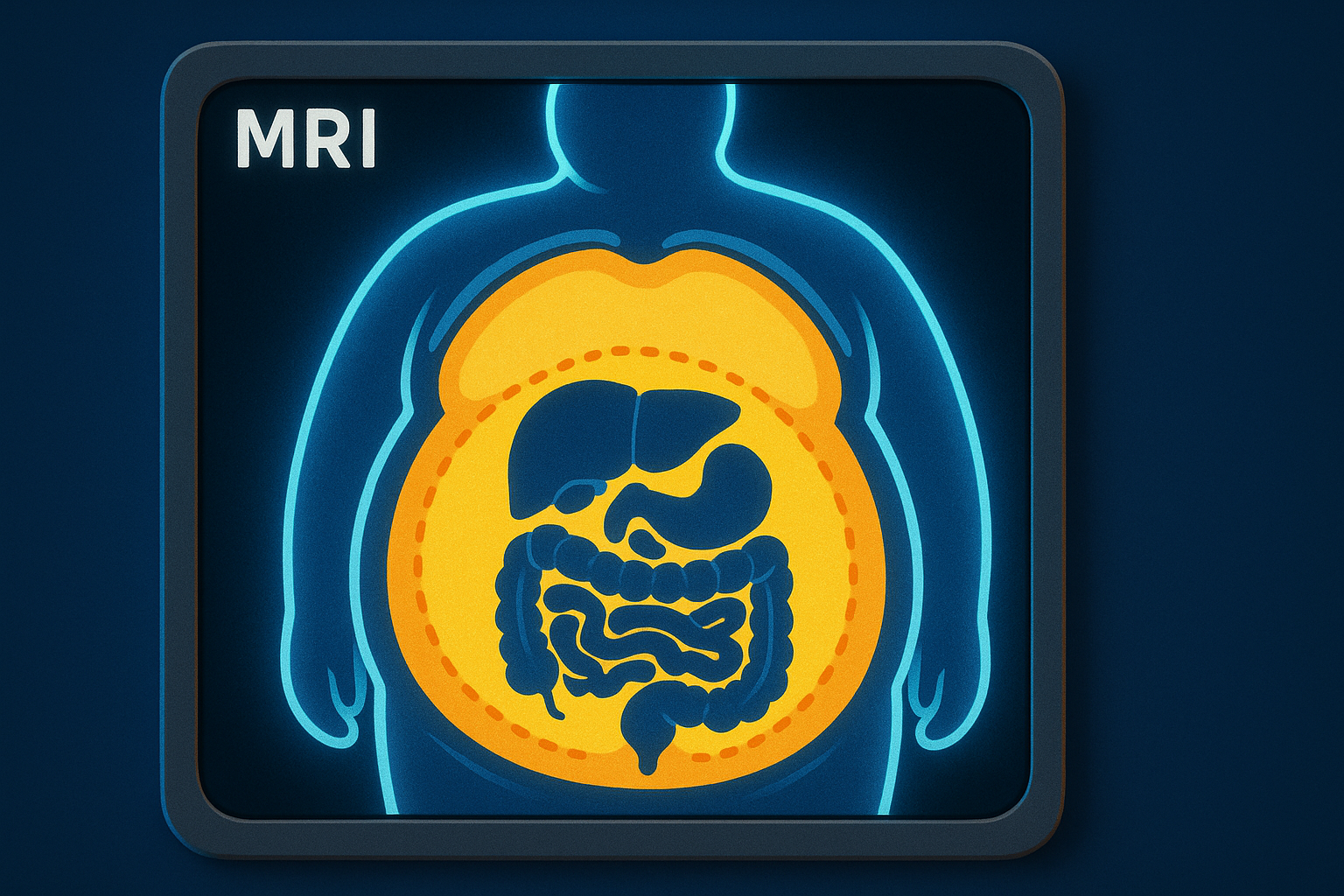
Hidden Visceral Fat Speeds Heart Aging Despite Exercise.
In 2025, Vladimir Losev and a team from the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences in London analyzed 21,241 UK Biobank adults, using AI to study body fat via whole-body imaging and heart health through scans. They focused on visceral fat (hidden around organs like the stomach) and its link to heart aging, measured by tissue stiffness and inflammation.
Exercise Slows Aging Clock in Multiple Organs.
In 2025, Takuji Kawamura and a team from Tohoku University reviewed studies on how exercise affects epigenetic aging, which shows how fast your body ages at the DNA level. They looked at human and animal research, focusing on structured workouts like running or weightlifting, using epigenetic clocks to measure DNA changes in blood, muscles, and other organs.
Creatine Plus Exercise Prevents Type 2 Diabetes.
In 2025, Ewelina Młynarska and a team from the Medical University of Lodz reviewed studies on creatine monohydrate supplementation combined with exercise for preventing type 2 diabetes. They focused on how skeletal muscle, which handles most body glucose, loses function in type 2 diabetes due to insulin resistance and sarcopenia (muscle wasting), and how creatine monohydrate—found in meat/fish or supplements—might help alongside workouts like weights or aerobics.
Speed Eating Linked to Poor Teen Mental Health.
In 2025, Yuko Fujita and Tomohiro Takeshima from Nagasaki University surveyed 106 adolescents and young adults (aged 12-24) in Japan. They used a lifestyle questionnaire and the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) to check mental health, and a gummy jelly test to measure swallowing threshold (how fast someone eats).
Exercise and Yogurt Cut Inflammation in Young Men.
In 2025, Emily C. Fraschetti and a team from York University studied 30 healthy young males in a 12-week trial. They did resistance and plyometric exercises twice weekly, with half consuming Greek yogurt (20g protein) and half an isoenergy carb pudding post-workout. They measured inflammation markers like IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP in blood at start, 6 weeks, and end.
Exercise Boosts Sleep Quality for Insomnia Sufferers.
In 2022, a team reviewed six studies with 295 adults to see how exercise helps insomnia. They found that regular workouts, like walking or yoga, improved sleep quality and cut insomnia severity by 20-30%, making it easier to fall and stay asleep.
Exercise 1.5 Times Better Than Drugs for Mental Health.
In 2023, Ben Singh and a team reviewed 97 meta-analyses covering 1,039 trials with 128,119 adults to compare exercise against psychotherapy or medications for mental health issues like depression and anxiety. They looked at various workouts—brisk walking, weights, yoga—measuring effects on mood, stress, and brain chemicals.
Sore Muscles Don’t Guarantee Muscle Growth.
In 2016, Sal Di Stefano from Mind Pump Media reviewed what sore muscles mean for fitness, drawing on exercise science. He explained that soreness, often linked to inflammation or lactic acid buildup, happens when you try new workouts or push too hard, not necessarily from effective training. For example, even advanced lifters get sore from unfamiliar activities like swimming, but this doesn’t mean better muscle gains.
Workouts Rival Medications for Depression Relief.
In 2021, Yumeng Xie and a team from Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University reviewed many studies on how exercise helps people with depression. They looked at different kinds of workouts like running, swimming, or yoga, and how they change brain chemicals, reduce swelling, and improve mood. Exercise works by boosting happy brain signals like serotonin and dopamine, growing new brain cells, and cutting down harmful stress.
Whey Protein Boosts Muscle Growth with Exercise.
In 2025, Xiaorong Ji and team from Shanghai University of Sport reviewed 21 studies with 1,200+ healthy adults. They looked at how whey protein, taken with exercise like weight lifting or running, helps build muscle. The studies compared groups using whey (20-40g per dose) to those doing exercise alone or with other proteins, measuring muscle protein synthesis (how muscles repair and grow) and the AKT/mTOR pathway, a cell signal that turns on muscle building.
Juice Powder Plus Exercise Cuts Inflammation in Obese Women.
In 2013, Manfred Lamprecht and team from Graz, Austria, studied 34 obese women in a 12-week trial. They split them into four groups: one got a fruit/vegetable juice powder concentrate, another got the powder plus exercise, a third just exercised, and the last got a placebo. They measured inflammation, oxidative stress, and blood flow markers.
Retirement Can Speed Up Health Decline Without Purpose.
In various studies from 2013 to 2023, researchers like those from the University of Manchester and NBER analyzed data from thousands of retirees in cohort and longitudinal setups. They tracked health changes post-retirement, focusing on cognitive, physical, and mental aspects, adjusting for age, job type, and voluntary status.
Running Literally Rewires Your Brain to Fight Alzheimer’s.
A 2024 study by Mass General Brigham found that exercise doesn’t just help memory—it actually activates specific genes that protect against Alzheimer’s. Mice with Alzheimer’s who used running wheels showed better memory, and scientists found that their brains had boosted activity in cells tied to blood vessels and immune defense.
Amino Acids Can Save Your Muscle While Losing Fat.
In 2025, Cannavaro, Leva, Caturano, Berra, Bonfrate & Conte (Université Clermont Auvergne & CNRS) reviewed research on using amino acid supplements during weight loss. Their Nutrients paper finds that certain amino acids—especially leucine, HMB, and collagen peptides—help protect lean mass when you’re slimming down.